Have you ever been so mad you felt flushed or experienced chest pains, headaches or some other physical manifestation of stress? If so, it might not come as a surprise to find out that the ability to exercise anger management may actually help increase your lifespan.
Anger comes with an injection of cortisol (stress hormone) and adrenaline into the bloodstream. This can cause muscle tension, severely increased heart rate and spikes in blood pressure.

These responses have significant consequences for the heart and the brain. Stress has been repeatedly correlated with heightened levels of C-reactive protein (CRP). Present in the blood, CRP is closely linked with inflammation, a well-known driver of aging and risk factor for events such as heart attacks and stroke.
Stress and, in particular, anger is more of a threat to our health as we age. A study published in Psychology and Aging notes that when subjects older than 80 regularly feel anger, they have increased levels of certain inflammation biomarkers. Older adults who experience elevated inflammation are more likely to have at least one chronic illness.

Can Anger Shorten Your Life?
The extreme anger associated with outbursts of rage increases the risk of heart attack and other significant health events. When you are in this state, your brain is no longer using the prefrontal cortex (area used for reasoning) for thought, but instead it is driven by the amygdala (the emotional center of your brain).
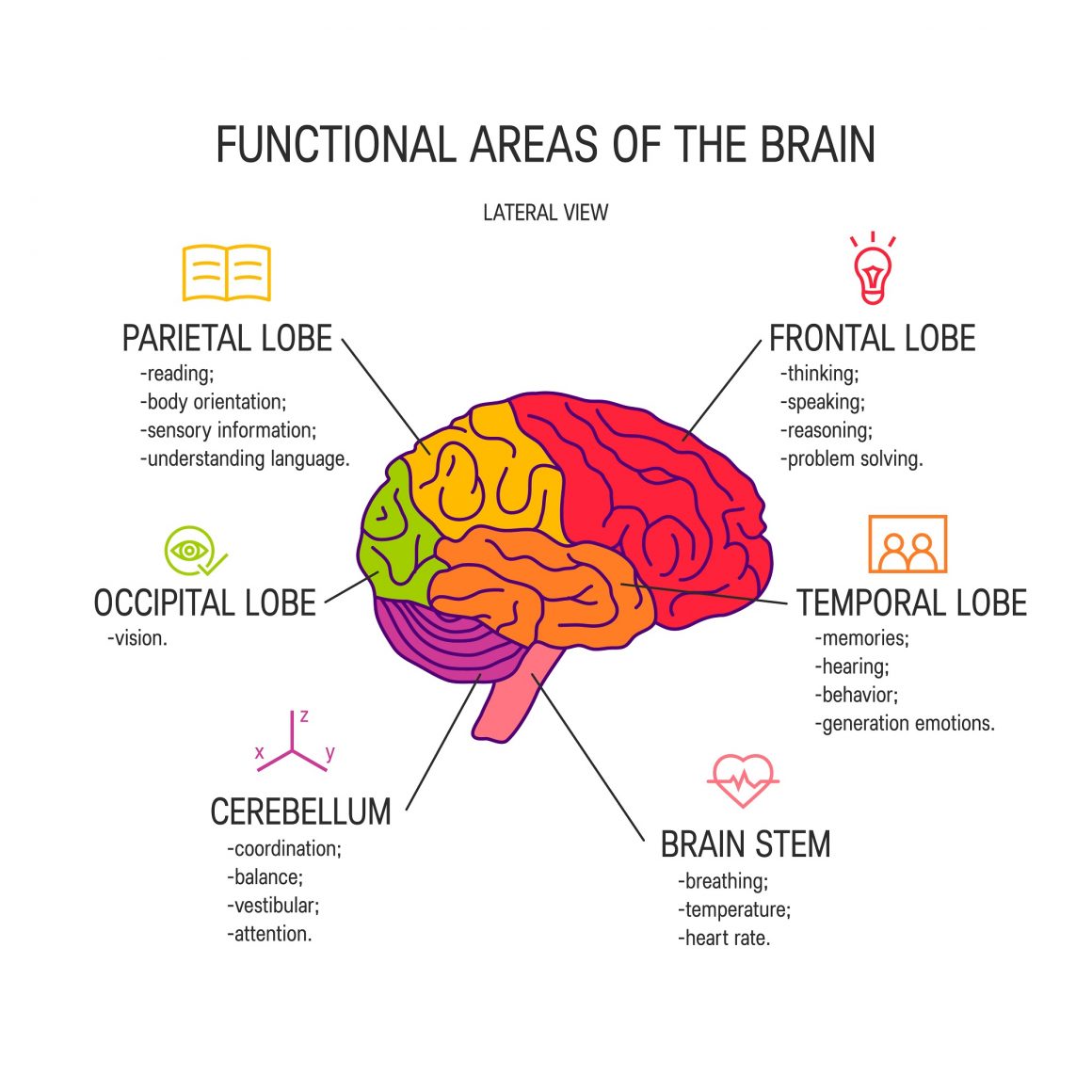
Logic, insight and facts all become blurry when the amygdala takes over and this can put significant strain on those around you as they attempt to communicate with you. Some people even report feelings of blacking out during such episodes and studies show that there is an increased risk of stroke resulting from a blood clot in these scenarios.
When you think of anger, however, it’s important to remember not just the big outbursts, but the ways in which this emotional state can permeate your everyday life and become chronic anger. Resentment is one of the many forms that anger may take due to the fact that publicly expressing your anger can also have a big effect on relationships.
Resentment can be an overwhelming sensation and dominate your thoughts, making it difficult to focus and cause a person to be less patient with others. This can feel like a loss of emotional control and manifest itself through pessimism and low self-esteem, which can lead to chronic conditions such as anxiety or depression.
Those suffering from chronic anger often experience lower lung capacity and suppressed immune systems as well. In a nutshell, stress and anger are directly tied to your health. Maintaining a healthy grip on these emotions is vital to longevity.
How Can I Control My Anger?
Some studies suggest that letting your anger out is not only healthy, but it will even add years onto your life. But in order to avoid explosions of anger, it is best to use some common anger management practices so that you express yourself in ways that are not only constructive for others, but healthy for you.

Some useful anger management techniques include:
- Deep breathing exercises to help you calmly express your emotions.
- Exercise to release tension and excess energy.
- Use humor to lighten your mood or break tension.
- Take a moment to enjoy silence. A bit of tranquility can do a lot of good.
- Avoid criticism or expressions that may heighten tension with others.
- Accept help from others in learning how to express yourself.
