The market for dietary supplements is well developed yet inconsistently regulated, leading to a variety of false claims about what supplements can provide for your overall health. One commonly discussed segment of the market is hormone supplements for antiaging, with some doubting their effectiveness and others sharing stories of dramatic improvements.
Research around the area of hormone supplements is ongoing, but some studies suggest positive results can be obtained, particularly when coupled with lifestyle changes. So, let’s take a look at some of the most common hormone supplements that are readily available at your local health foods store and see whether or not the science matches the claims made by manufacturers.
DHEA
Short for dehydroepiandrosterone, DHEA is produced in the adrenal glands and is the precursor for testosterone, estrogen, and progesterone. Studies examining DHEA’s role in the aging process are motivated by the fact that DHEA levels decline as we age, severely impacting energy and stress levels, particularly in postmenopausal women.
There’s some evidence to suggest that DHEA supplements can help improve quality of sleep, while increasing energy levels and the ability to handle stress. It binds to varying types of receptors within the brain to have a positive impact on symptoms of depression, memory loss, and cognitive decline.
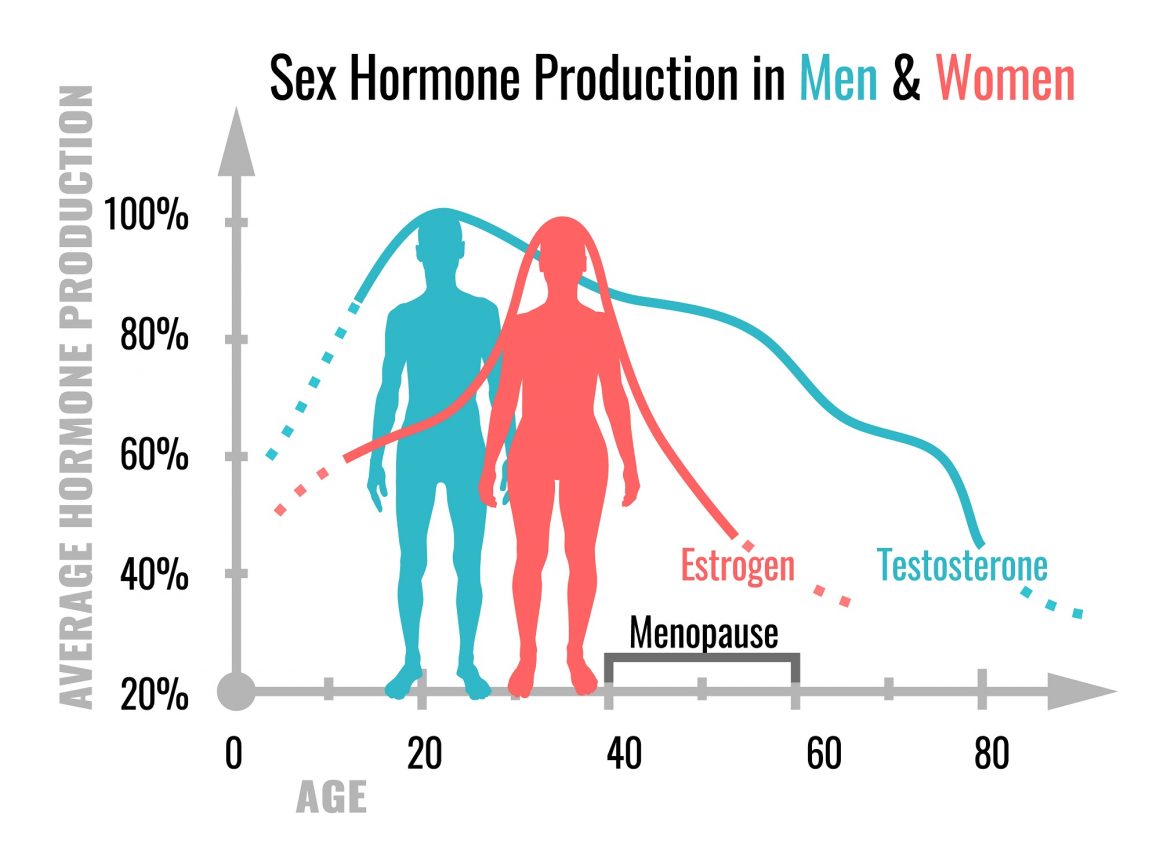
Testosterone
As the hormone at the center of men’s health, there is a temptation to believe that age related conditions can be treated by increasing testosterone levels in males. Low testosterone has been linked to low muscle mass, osteoporosis, cognitive impairment and even Alzheimer’s disease. Testosterone replacement therapy has been shown to be beneficial in men when it comes to bone density and cognitive function in the areas of spatial, verbal and working memory and executive function.
But those hyping testosterone as a wonder supplement for elderly men ignore some important facts, chief among them that decreases in testosterone levels happen gradually and supplementing testosterone has not been found to be helpful in men who have normal levels of the hormone for their age.
Estrogen
Tests concerning hormone replacement therapy in women is mostly driven by the potential of easing the symptoms of menopause. Vaginal dryness and reduced sexual pleasure affect two-thirds of women during perimenopause, the transitional phase that begins several years before menopause begins. In some cases, the severity of these symptoms is such that it can interfere with daily activities and disrupt sleep patterns.
Estrogen may be administered by itself or together with progesterone. It can provide relief from some menopause symptoms, and prevent vaginal atrophy. It may also have a positive effect on bone loss and risk of developing colon cancer.
The news isn’t all good though. The Women’s Health Initiative (WHI) conducted the largest study on this topic and showed evidence that the risk of breast cancer, stroke, cardiovascular disease, and events tied to deep vein blood clots increased. Hormone replacement therapy is therefore a serious thing to consider before taking any action, with any decision made being done in accordance with your doctor’s recommendations.
Melatonin
Much of the interest in melatonin is based on questionable assumptions that say melatonin levels decrease naturally with age. We’ve looked at the impact of melatonin, highlighting its potential for addressing sleep disorders and noting its potential to impact other areas of brain and skin health.
For more on melatonin, read: Can Melatonin Supplements Slow Down Aging?
Growth Hormone
Growth hormone in humans plays an important part in regulating muscle and fat mass, lipids, glucose, and overall well-being. It’s a big concern for elderly populations as growth hormone levels drop by 14% each decade, according to a paper from Dr. Michael Klentze, President of the European Council on Aging Research and Education.
Symptoms of growth hormone deficiency include decreasing muscle mass, increased risk of obesity, brain atrophy, osteoporosis and dysfunction in the immune system. Growth hormone treatments can be effective; however, they can also be quite expensive.